Unraveling the Threads: A Deep Dive into Vortex Yarn vs. Ring-Spun Yarn
2025-07-17
In the vast world of textile manufacturing, yarn production methods have a profound impact on the final fabric’s feel, durability, and performance. Among the various spinning techniques, vortex spinning and ring spinning stand out as two widely used processes, each with unique characteristics. Understanding the distinctions between vortex yarn and ring-spun yarn is essential for textile professionals, designers, and even consumers looking for specific fabric qualities.
1. Introduction to Spinning Methods
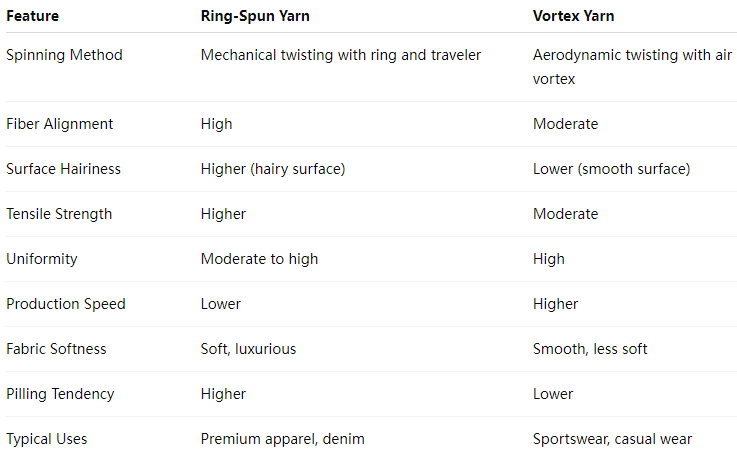
Ring Spinning is one of the oldest and most traditional methods of yarn production, dating back to the 19th century. It involves drafting fibers and twisting them around a spindle using a ring traveler, resulting in yarn with high strength and smoothness.
Vortex Spinning, on the other hand, is a relatively modern innovation introduced in the late 20th century. It uses a high-speed air vortex to twist fibers into yarn, eliminating some mechanical contact found in traditional spinning and aiming to increase production speed and reduce costs.
2. How Are They Made?
Ring-Spun Yarn Process:
Fiber Drafting: Fibers are carefully drafted to align and thin out the fiber strand.
Twisting: The drafted fibers pass through a ring and traveler system, where twisting occurs as the spindle rotates. The traveler moves around the ring, imparting twist to the fibers.
Winding: The twisted yarn is wound onto a bobbin.
This process produces yarn that is tightly twisted, which enhances strength, durability, and uniformity.
Vortex Yarn Process:
Fiber Feeding: Fibers are fed into a high-speed rotating rotor.
Air Vortex Twisting: Inside the rotor, an air vortex is generated. The fibers are twisted by aerodynamic forces rather than mechanical twisting.
Winding: The resulting yarn is continuously wound onto a package.
This method reduces mechanical friction and allows for much higher spinning speeds compared to ring spinning.
3. Structural and Physical Differences
Fiber Alignment: Ring-spun yarn typically has better fiber alignment due to the controlled drafting and twisting process. Vortex yarn fibers tend to be more randomly oriented, especially on the yarn surface.
Hairiness: Ring-spun yarn is known for its characteristic surface hairiness, which contributes to the fabric’s softness and aesthetic appeal. Vortex yarn is smoother and has less surface hair because the aerodynamic twisting pulls fibers inward.
Tensile Strength: Ring-spun yarn usually has higher tensile strength because of the strong mechanical twist and fiber cohesion. Vortex yarn has good strength but may be slightly lower in tensile strength due to the different twisting mechanism.
Uniformity: Vortex yarns tend to have fewer thick and thin places and better uniformity because the process can eliminate certain irregularities found in ring-spun yarn.
4. Performance and Fabric Characteristics
Softness and Hand Feel: Ring-spun yarn fabrics are softer and more luxurious, favored in high-quality garments and premium textiles. Vortex yarn fabrics feel smoother but slightly less soft, making them suitable for sportswear and functional textiles.
Durability: Ring-spun yarn is highly durable and abrasion-resistant, ideal for products requiring long wear life. Vortex yarn’s slightly lower abrasion resistance limits its use in heavy-duty applications but excels in comfort and breathability.
Pilling: Fabrics made from ring-spun yarn tend to pill more because of surface hairiness, whereas vortex yarn fabrics are less prone to pilling due to reduced hairiness.
Cost and Productivity: Vortex spinning is faster and more cost-effective, allowing manufacturers to produce yarn at a higher rate with lower labor and energy costs. Ring spinning, though slower and more labor-intensive, yields premium yarn with superior quality.
5. Environmental and Economic Considerations
Vortex spinning’s higher speed and lower energy consumption can offer environmental benefits by reducing carbon footprint. The reduced labor requirements also make it economically appealing for mass production. Ring spinning, while less efficient, produces premium quality that can justify the environmental and cost inputs in luxury markets.
6. Summary Table of Differences
7. Conclusion
The choice between vortex and ring-spun yarn depends largely on the end use of the fabric and the balance between cost, quality, and performance. Ring-spun yarn remains the gold standard for luxury textiles due to its softness, strength, and aesthetic appeal. Meanwhile, vortex yarn provides an efficient, cost-effective alternative for producing smooth, durable fabrics suited for everyday and activewear applications.
Both yarn types have carved important niches in the textile industry, driven by their unique spinning technologies and resulting fabric characteristics. Understanding these differences helps textile manufacturers, designers, and consumers make informed decisions to meet specific performance and aesthetic goals.



 English
English русский
русский Español
Español 中文简体
中文简体

















